Implementing AI in Manufacturing: Benefits, Challenges, and Proven Results
The adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies is accelerating change in the manufacturing sector. Companies are shifting from basic production systems to smart, automated operations powered by data.
In this context, AI refers to systems that can process and analyze enormous volumes of manufacturing data, recognize trends, and make independent decisions. A more recent development, Generative AI (GenAI), goes further by using neural networks to create content – such as instructions or simulations – that can expedite industrial progress.
The impact of AI cannot be overstated. It’s no longer just speculation. According to the Grand View Research, an overwhelming 93% of manufacturers identified AI as one of the top innovations driving productivity in the coming years. Its applications range from predictive maintenance to automated quality control – and so does the competitive pressure to adopt them.
In this article, we explore six use cases backed by real-world examples that highlight the many advantages of AI in manufacturing.
We’ll also present raw data on how businesses are overcoming implementation challenges.
Additionally, we’ll include a case study showcasing how Mobilunity supported a client from the manufacturing industry by providing AI specialists to accelerate their digital transformation.
Top 6 AI Use Cases in Manufacturing
Below you can explore the top AI use cases in manufacturing, including predictive maintenance, quality control, and supply chain optimization, to see how smart tech boosts efficiency and cuts costs.
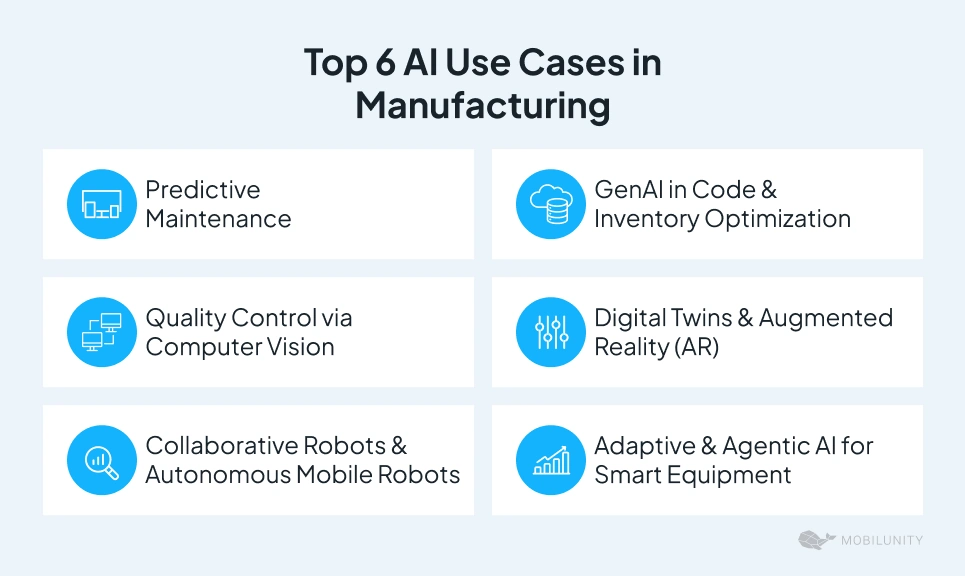
Predictive Maintenance
One of the earliest and most valuable applications of machine learning in the manufacturing business is predictive maintenance. These AI systems use anomaly detection and forecast failures by analyzing sensor data – such as vibration, temperature, and pressure.
For instance:
- Siemens uses AI to predict mechanical wear and optimize machine uptime, reportedly reducing global unplanned downtimes by $1.4 trillion.
- Aquant leverages AI to analyze service data and guide technicians through real-time diagnostics, improving both accuracy and response time.
- Gecko Robotics deploys AI-powered inspection robots that scan machines for micro-defects too small for human detection.
Manufacturers that adopt AI for maintenance have seen a reduction in unplanned downtime, an increase in equipment lifespan, and more precise maintenance schedules.
Quality Control via Computer Vision
Quality assurance has long struggled with speed, consistency, and cost. Traditional methods now face competition from computer vision powered by AI algorithms. These systems use deep learning frameworks and high-resolution cameras to monitor assembly lines in real time – often outperforming human inspectors in both speed and accuracy.
For example:
Ford, in partnership with Google Cloud and other industrial AI providers, implemented vision-based inspection systems. This improved the accuracy of torque converter installation by 15% and reduced production delays. Cross-industry collaborations have enabled tools like TAQFC’s monitoring system to assess feature performance and measure productivity using advanced algorithms that track preset processes.
Product-driven companies like Foxconn and Panasonic now rely on deep learning vision systems to scan each product for surface-level flaws. This approach significantly reduces defect rates, resulting in fewer recalls and less waste.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots) & Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
With the rise of smart automation, technologies like Collaborative Robots (Cobots) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are now capable of handling more advanced tasks thanks to AI.
Cobots work alongside humans, taking over repetitive or ergonomically challenging tasks. AMRs, on the other hand, navigate factory floors independently, transporting materials to designated areas.
One remarkable example:
A bakery in Queensland implemented AI-powered collaborative robots for packing and logistics. As a result, human workers shifted to more complex tasks, and the business doubled its production capacity.
AI-powered robots have become more flexible and responsive to their surroundings. They’re now safer, faster, and more easily adaptable to operational changes.
GenAI in Code & Inventory Optimization
Generative AI is being widely adopted in production environments for tasks such as:
- Debugging machine code: GenAI tools assist engineers with Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) by generating and refining machine code.
- Inventory optimization: GenAI processes supply chain data and sales patterns to predict demand and calculate ideal stock levels, enabling smarter procurement and reducing costs.
According to a 2024 TechTarget study, companies using GenAI for inventory planning reduced stockouts by 18% and cut excess inventory by 21%.
This type of digital intelligence enhances speed, scalability, and strategic planning across smart manufacturing operations.
Digital Twins & Augmented Reality (AR)
Digital twins are real-time virtual replicas of physical assets – such as equipment, factory layouts, or production lines – fed by IoT and AI data. These models help engineers forecast performance and simulate changes, reducing disruption during testing phases.
Paired with AR goggles, generative AI delivers maintenance instructions projected directly onto machinery. This hands-free approach guides technicians through repairs or setup tasks in real time.
Automotive companies like BMW and Volvo have adopted AR with GenAI-powered diagnostics to streamline technician onboarding and reduce human error.
Adaptive & Agentic AI for Smart Equipment
Adaptive or agentic AI systems modify their responses based on real-world inputs – such as material changes, temperature shifts, or updated production goals. These smart machines represent the next phase of evolution in manufacturing.
Siemens, a leader in smart equipment, integrates agentic AI into its systems. This has led to more than 25% downtime reduction and significant energy efficiency gains.
Adaptive AI tools also enable mass customization – allowing factories to manufacture varied products without halting production or compromising quality.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in the Manufacturing Industry
Integrating AI into manufacturing isn’t just about keeping up with technological trends. It’s a strategic move that brings clear advantages across every step of production.
From improving operational resilience to optimizing inventory management, AI helps manufacturers boost efficiency and stay competitive.

Reduced Downtime & Maintenance Costs
Unplanned equipment breakdowns can halt entire production lines, leading to significant financial loss. AI-powered predictive maintenance enables anomaly detection and early issue resolution. This proactive approach reduces downtime and extends equipment life.
Industry data shows that predictive maintenance powered by AI cuts maintenance costs by an estimated 25% and reduces unplanned outages by nearly 50%.
Quality & Safety Gains
AI-based computer vision systems have revolutionized quality control. These systems inspect defects with high speed, accuracy, and consistency – surpassing traditional methods and minimizing costly recalls.
The power of AI can also predict potential safety risks and automates hazardous tasks, helping enforce safety standards. Companies applying AI to quality and safety have seen a significant drop in product faults and fewer workplace incidents, as reported by Wired.
Efficiency & Productivity
AI dramatically enhances business process automation. Cobots (collaborative robots) handle repetitive or physically demanding tasks, while AR (augmented reality) helps train workers with step-by-step guidance. The result is faster assembly, fewer errors, and less rework.
For example, Jabil Circuit Inc. combined precision processes with AI automation, leading to significant productivity improvements. Real-world outcomes show that merging AI with traditional workflows delivers tangible performance gains.
Forecasting Tools & Technologies
Supply chain management is one of the primary cases used in manufacturing.
AI enhances forecasting by processing vast datasets in seconds. These systems accurately predict demand trends and optimize stock levels, reducing overstock and stockouts. As a result, supply chains become shorter, and cash flow improves.
AI-powered forecasting tools also improve agility for firms managing stockpiles, allowing smarter planning and real-time market adaptation.
Workforce Upskilling
Rather than replacing humans, Artificial Intelligence in manufacturing often enhances their roles. By automating repetitive tasks, employees can shift focus to more creative and strategic functions.
A case in point: a Queensland bakery used AI-enabled cobots to improve packaging. This freed staff to retrain in logistics planning and quality control, as reported by The Australian and Business Insider.
AI empowers teams by supporting skill development and enabling smarter workforce deployment – enhancing both operational capability and employee retention.
Key Challenges in Implementing AI in Manufacturing
Despite the clear benefits, several obstacles stand in the way of AI adoption in the manufacturing industry. These challenges – structural, technological, and cultural – must be addressed to unlock AI’s full potential.
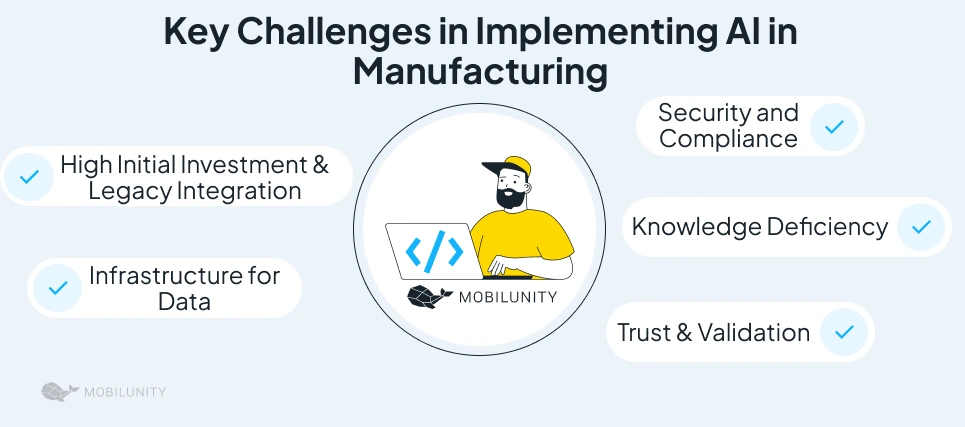
High Initial Investment & Legacy Integration
The biggest barrier is cost. Implementing AI – from hardware and software to hiring and system upkeep – requires major investment, particularly for small manufacturers.
Legacy systems often lack compatibility with AI applications in manufacturing. Retrofitting them or building custom APIs drains time and resources, slowing deployment. Without a clear modernization strategy, companies risk building on outdated foundations, limiting future scalability.
Infrastructure for Data
AI runs on data – but not just any data. It needs clean, well-labeled, structured data to perform accurately. Unfortunately, many manufacturing facilities lack proper infrastructure to support real-time data collection and analysis.
Codasol highlights common issues like inconsistent formats, missing values, or noisy sensor data – all of which undermine AI performance. To avoid this, companies must invest in governance frameworks, data monitoring tools, and reliable pipelines for real-time streaming.
Knowledge Deficiency
A major challenge is the shortage of AI expertise. Manufacturing AI capabilities focus on the intersection of machine learning, data engineering, and industrial operations – a rare skill set that’s hard to find and even harder to retain.
Over 60% of industrial firms cite AI talent gaps as their top concern, according to recent studies. To close this gap, companies should upskill existing teams, bring in external consultants, or partner with niche providers like Mobilunity.
Security and Compliance
With AI and IoT integration, cybersecurity risks multiply. Every new digital endpoint becomes a potential vulnerability – raising the stakes for data breaches or model manipulation.
In addition, stricter regulations around privacy, ethics, and AI usage place added pressure on legal and IT teams. Manufacturers must stay compliant with industry standards, which vary across regions.
To stay safe and compliant, companies need strong ethical frameworks, robust cybersecurity protocols, and routine audits.
Trust & Validation
Generative AI introduces unique challenges around trust. While it can automate tasks like documentation or code generation, it also risks producing incorrect or misleading outputs – often called hallucinations.
TechTarget and Codasol both stress the need for human validation in critical industrial settings. Over-reliance on unchecked AI can result in flawed workflows, compliance issues, or even production hazards.
AI brings enormous value – but implementation must be thoughtful, well-resourced, and carefully managed. Companies that meet these challenges head-on will be best positioned to reap long-term rewards.
Mobilunity Case Study: Employing AI Engineers for Efficient Manufacturing Processes
At Mobilunity, we understand that many manufacturing companies struggle to align their business operations with advanced technologies like AI.
Integrating these innovations into existing workflows is challenging. That’s why we specialize in helping industrial clients hire skilled AI developers and data specialists – efficiently and at scale.
Client Overview & Challenges
A Europe-based manufacturing firm came to Mobilunity aiming to boost production efficiency through AI automation. Their vision included predictive maintenance, advanced inventory control using Generative AI, and PC-based automation of quality assessments via computer vision algorithms. However, they faced several obstacles:
- Lack of internal AI and machine learning expertise
- Inability to integrate AI with legacy systems
- No capacity for real-time analytics
- High costs of local recruitment
They needed a vendor capable of quickly building a multidisciplinary team with expertise in machine learning, data engineering, computer vision, and industrial automation.
Mobilunity’s Approach
Mobilunity deployed its dedicated development team model to provide a tailored solution.
We contracted AI/ML developers and data engineers from Ukraine, balancing technical skill with cultural fit.
The team members we hired brought relevant experience in manufacturing industries and IoT embedded systems, which accelerated onboarding.
They work remotely (cooperation is ongoing), while fully integrating with the client’s R&D, operations, and IT departments, participating in daily standups, sprint planning, and code reviews.
Mobilunity also managed payment processing, HR support, and infrastructure help desk. This allowed the client to focus solely on delivery and results.
Results & Impact
Over nine months, Mobilunity’s AI developers became a trusted part of the client’s team. They worked side by side with in-house staff to bring several AI projects to life:
- Inventory optimization. Using AI to forecast demand, the client improved how they managed stock. This helped avoid overordering and made better use of storage space.
- Predictive maintenance. The team built models that track machine health and flag early signs of wear. This gave the client time to plan repairs and avoid sudden breakdowns.
Throughout the process, Mobilunity provided more than just developers – we offered project continuity, technical specialists with relevant expertise, and flexible scaling when needed. Our support helped the client stay on track, meet development goals while building confidence in AI-driven change.
Why Mobilunity?
- Talent anywhere, work where you are. Mobilunity removes local hiring cost barriers, giving you access to global experts without compromising quality.
- Domain-specific expertise. Engineers we hire understand the unique challenges of industrial environments.
- Scalable & flexible engagements. Need one AI engineer or a full team? We scale to match your growth and requirements.
From initial AI prototypes to full-scale industrial solutions, Mobilunity offers timely, strategic, and budget-friendly AI hiring services tailored to your manufacturing needs.
Disclaimer: All salaries and prices mentioned within the article are approximate numbers based on the research done by our in-house Marketing Research Team. Please use these numbers as a reference for comparison only. Feel free to use the contact form to inquire on the specific cost of the talent according to your vacancy requirements and chosen model of engagement.