Top Technology Trends in the Insurance Industry that Drive Growth and Innovation
From AI-powered underwriting to blockchain-based claims management, digital advancement encourages transformative changes across the insurance field and allows businesses to save costs. However, technology implementation still poses challenges.
We’ve reviewed reports from McKinsey and Deloitte to explore how companies start driving growth through insurance modernization. We’ll discover how current AI technologies can boost this industry in 2024-2025 and discuss their limitations.
AI in the Insurance Industry
Artificial Intelligence penetrates every aspect of business operations, and the insurance sector is no exception. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of complex data, allowing companies to boost claims handling, enhance risk assessment, automate underwriting, detect fraud, and personalize customer experiences.
AI-driven insurance technology trends significantly impact core insurance processes, business models, and strategies.
Insurers introduce Artificial Intelligence into various insurance models to deliver products faster, manage risks better, and meet their business goals sooner.
Below, we’ll explore AI-powered technology trends in the insurance industry in more detail and learn how they add business value.
Here are a few use cases of how AI facilitates insurance workflows.
| Process | How AI Helps |
| Advanced Underwriting | – Automates risk assessment with AI-driven predictive models – Provides more accurate pricing by analyzing vast datasets in real time |
| Fraud Detection | – Identifies subtle fraud patterns with ML algorithms – Reduces false positives and minimizes fraudulent payouts |
| Personalized Customer Experience | – Empowers AI-driven chatbots for 24/7 customer support – Enables tailored policy recommendations based on customer behavior |
| Claims Automation | – Analyzes photos and videos to assess the damage and estimate the payout – Prioritizes and routes pre-processed claims to appropriate teams or systems |
Challenges of Implementing AI in Insurance
Despite the significant benefits AI offers to insurers, this insurance industry trend also brings notable limitations.
Dependence on Quality Data
AI models require accurate, comprehensive, and objective datasets to produce reliable outcomes. Incomplete or inconsistent data can lead to flawed predictions, reduce transparency, introduce bias, and result in non-compliance with regulations. So, insurers must continuously clean, standardize, and enrich data to take full advantage of AI.
AI Ethics in Underwriting
AI algorithms often rely on historical data that can include biases and potentially lead to discrimination based on race, gender, or socioeconomic factors. Companies must run regular model audits and fairness testing and ensure adherence to ethical frameworks to build trust and secure equitable underwriting practices.
Explainability of Algorithms
Due to the “black-box” nature of AI systems, especially complex ones, it’s sometimes difficult to understand the reasons behind their decisions. Without a clear justification, AI’s choices may result in unfair treatment and lower trust of policyholders or lead to reputational damage or legal issues.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Adoption in Insurance
RPA is used in the insurance industry to streamline rule-based tasks, improve the accuracy of data input, and grow team productivity.
You can hire RPA developers to create bots that enable:
Faster Claims Processing
RPA scripts can extract information from claim forms, emails, or documents and upload it to insurance systems. They can classify claims based on rules in insurance policies and send simple cases for immediate processing while routing complex ones to humans.
Robotic algorithms can collect and verify data from medical reports, repair estimates, etc., checking alignment with claims requirements.
Automatic real-time status updates and notifications, and payment triggering enhance customer satisfaction and transparency.
Preparation of Onboarding Reports
RPA tools can extract data from government databases, financial records, and customer documents in real time. They validate clients’ ID proofs, income statements, and physical addresses, ensuring adherence to Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations.
Robotic processes can integrate with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) databases to screen customers against global watchlists, sanctions, and politically exposed persons (PEP) lists, immediately flagging potential risks.
Automated workflows can help insurance agents compile relevant data into KYC and AML compliance reports, ensuring accuracy and timely submission.
Effective Policy Management
RPA automates policy creation by retrieving and verifying customer insurance data. Scripts can also run timely renewals, refresh terms, and process payments.
This technology automates updating contract information, adding new coverage, modifying beneficiaries, etc. RPA assists them with uploading, sorting, and indexing policy documents.
RPA Limitations and Solutions
Though robotic process automation offers significant advantages to the insurance industry, complex or non-standard processes have become challenging for this technology.
For instance, RPA tools struggle with processing handwritten forms or documents in various formats. However, advanced integration with AI and OCR (Optical Character Recognition) allows for addressing such scenarios.
Automation bots may not adapt well to exceptions, so scaling RPA across complex operations may require utilizing machine learning or artificial intelligence.
Blockchain Technology for Better Transparency
Another innovation in the insurance industry is distributed ledger technology (DLT), or blockchain that enables smart contracts and prevents insurance fraud.
Insurance providers and policyholders agree on the terms (coverage, premiums, triggers) and encode them into a self-executing (smart) contract on a blockchain network.
Such contracts have access to IoT devices, weather APIs, databases, and other data sources, so users can monitor them live.
Once the condition is met and verified, smart contracts execute payments automatically, enhancing accuracy, transparency, and processing times.
Blockchain allows insurance carriers, brokers, and reinsurers to access a single source of truth. It also helps automate premium calculations, compliance checks, and payouts.
Below are the ways blockchain can streamline insurance operations:
| Problem | How Blockchain Helps |
| High fraud costs | – Creates a tamper-proof ledger for transactions, ensuring all claims and policy changes are checked and recorded – Shares ledgers among insurers, allowing them to spot duplicate or fraudulent claims and enhance cross-company collaboration |
| Coverage terms disputes andlack of clarity in policies | – Consolidates and provides access to immutable records of claims, endorsements, and policy terms to customers – Enhances trust between policyholders and insurance providers by fostering data integrity and immediate access |
| Complex data sharing and reconciliation in reinsurance agreements | – Allows for instant sharing of claims, premiums, and policies between insurance carriers and reinsurers – Speeds up calculations of payouts and risk-sharing agreements |
| Disputes over claim triggers (and amounts) based on predefined parameters | – Uses smart contracts to execute payouts based on objective parameters (specific weather conditions, natural disasters, economic indicators) – Eliminates the need for manual claim submissions |
| Time-consuming and debatable claims management | – The blockchain technology automatically initiates payouts once certain conditions are met – Automates verifications and payments, reducing settlement times |
| Significant administrative overheads | – Connects all parties directly, eliminating the need for intermediaries – Creates a single, transparent database that simplifies compliance and auditing, reducing operational expenses |
Blockchain Limitations
Despite blockchain’s transformative potential in the insurance industry, it comes with a few constraints.
High Implementation Costs
Setting up the blockchain infrastructure, such as decentralized networks, servers, and storage systems, requires significant costs. Additionally, you’ll need to hire blockchain engineers to develop, integrate, test, and deploy your solution.
Your distributed system also must comply with insurance regulations and GDPR, HIPAA, or other data protection laws. This implies engaging additional resources for legal reviews and system adjustments.
Poor Scalability
Each data unit (block) can handle a limited processing capacity, and with large and complex data, the network becomes congested. So, the growing number of users and claims will result in longer processing times and higher transaction costs.
Many blockchain platforms rely on the computational intensive Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanisms to validate operations. Higher transaction volumes can create bottlenecks that may compromise security.
Low Compatibility
Insurance companies often use decentralized legacy IT systems that require significant customization to integrate with blockchain networks. Moreover, they store data in unstructured formats that aren’t supported by distributed systems.
Additionally, new blockchain platforms evolve with their own protocols and architectures, which implies issues with interoperability.
B3i (Blockchain Insurance Industry Initiative) addressed this problem and tried to create a collaborative platform that facilitates data access, exchange, and management for insurers, reinsurers, and brokers. However, due to insufficient funding, the project was closed.
How Predictive Analytics and ML Are Reshaping the Insurance Landscape
Predictive analytics help insurance companies leverage data and advanced algorithms to forecast future events and new trends. Such analysis helps insurers optimize operations, boost decision-making, and improve customer experience.
Below are the examples of how predictive analytics impacts insurance processes:
1. Enhanced Risk Assessment
Statistical algorithms analyze customer behavior, historical data, and external factors like weather conditions or credit scores to forecast potential claims.
This facilitates accurate pricing and reduces underwriting errors. For instance, health insurance companies can save significant costs by checking customers’ medical history.
2. Fraud Detection and Prevention
Predictive models analyze claims and compare them to customer behavior, historical reimbursement requests, and external data. They detect abnormal patterns, unusual transactions, and other inconsistencies.
Models continuously learn and adapt, combining policy data with information from recordings or social media, delivering fraud insights, and allowing insurance businesses to combat double-dealing.
3. Improved Customer Retention
Algorithms identify customers at risk of lapsing through delayed payments, reduced engagement, and other patterns. Then, AI offers loyalty programs, customized discounts, upgrades, or personalized insurance services to retain policyholders.
Successful retention efforts and customer-centric approaches result in lower CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost) and higher trust in insurance organizations.
4. Catastrophe Modeling for Reserves
With the cat modeling tools, many insurance companies assess potential losses from human-caused events, natural disasters, pandemics, etc. These models estimate negative scenarios, evaluating their frequency, severity, and geography.
So, predictive AI in insurance allows agents to grow resilience against disasters, allocate sufficient reserves, and empower their underwriting decisions with data while minimizing financial losses.
5. Claims Forecasting and Management
Predictive tools can analyze economic trends, regional events, and weather data to evaluate peaks in claim volumes. Accurate forecasting lets insurers allocate resources and improve response times at high workloads.
Such a proactive approach impacts the way insurance companies operate during high-demand periods. They optimize staff management, reduce delays, and keep customers happy.
Limitations of Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics offers significant potential in insurance but faces limitations that impact accuracy, regulatory compliance, and equitable decision-making.
Managing Unstructured Data
Insurance companies collect large volumes of records that need format unification for predictive analytics. Unstructured data often contains noisy information like typos, irrelevant comments, or duplicate entries that can screw projections.
Predictive algorithms often have difficulties extracting meaningful insights from text-based content like policy documents and claim descriptions. They may struggle to detect context, sentiment, or specific terminology.
Solution: implementing NLP (Natural Language Processing) tools for text mining, using data lakes for preprocessing, and introducing ML models for heterogeneous datasets.
Handling Incomplete Data
Missing data affects predictive models’ ability to identify patterns and relationships, which leads to less accurate risk forecasting or premium calculations.
Additionally, incomplete datasets leave room for biases and inconsistencies that lead to inefficient decisions like rejecting valid claims, misidentifying fraud, or setting inappropriate premiums.
Solution: introducing ML algorithms to estimate missing values and work with partial inputs, enhancing data collection, and running regular data pipeline audits.
Non-Compliance with Regulations
Insufficient anonymization or improper PII (Personally Identifiable Information) handling in predictive analytics can violate privacy laws.
Biased, unverified, or incomplete data or credentials collected without explicit consent, especially when transferred between regions, may breach HIPAA, CCPA, GDPR, ICPs, Solvency II Directive, and other regulations.
Solution: automating data anonymization, monitoring cross-border data transfers, and identifying errors and biases with ML algorithms and RegTech (Regulatory Technology) tools integration.
Why Predictive Analytics Needs ML
Predictive analytics improves risk assessment, customer retention, fraud detection, etc. However, ML complements and amplifies its capabilities by enabling more precise, adaptive, real-time, insightful, and robust analysis.
Here’s how it works.
| Process | Predictive Analytics | Machine Learning |
| Risk assessment | Struggles with large, unstructured datasets (e.g., images, text, or IoT data) | Handles complex dynamic datasets, uncovering non-obvious patterns |
| Customer retention | Relies on structured, past data | Analyzes customer interactions, providing a more holistic view of policyholders’ sentiments |
| Data processing | Process complex, nonlinear relationships with moderate precision | ML techniques like neural networks or ensemble learning provide higher accuracy |
| Fraud detection | Identifies patterns based on preset rules | Detects subtle anomalies or emerging fraud patterns that evolve |
| Risk personalization | Uses historical data | Analyzes multiple variables (customer behavior, historical claims, location) simultaneously |
| Real-time predictions | Focus on periodic reports | Offer real-time insights, allowing insurers to act immediately |
While predictive analytics provides useful insights based on past data, ML has become an invaluable technology in the insurance industry in 2024. That’s due to its live analysis, dynamics, adaptability, and accuracy.
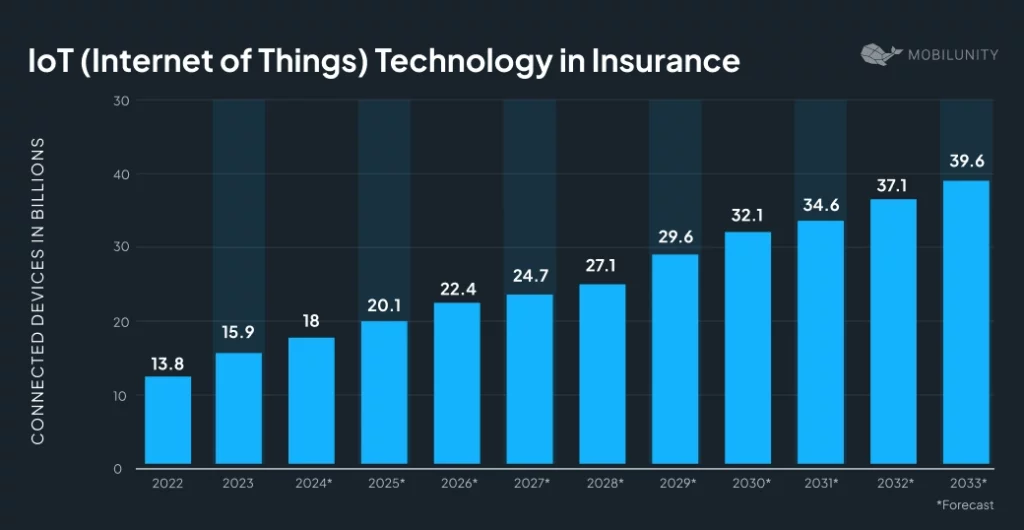
Source: Statista
The Internet of Things is among the new technologies that embrace the future of insurance, and its role in the industry will only expand. The number of connected devices is expected to grow from 18 billion in 2024 to 39.6 billion in 2033.
Here are some of its use cases:
- Auto insurance. Companies customize insurance offerings based on pay-as-you-drive or pay-how-you-drive plans by monitoring driving patterns through telematics. They consider individual risk factors and introduce fairer pricing in usage-based insurance (UBI), providing safer drivers with lower premiums.
- Medical insurance. Wearable devices can facilitate real-time premium calculations by monitoring policyholders’ lifestyle habits and health. Fitness trackers and smartwatches allow insurers to track heart rate, stress, sleep patterns, etc., and identify early health risk signs, promoting personalization.
- Property insurance. Smart locks, motion and smoke detectors, water leak sensors, HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, etc., are technology solutions that help insurers adjust premiums in the moment, prevent damage, and speed up claim verification. Companies can customize policies based on individual property risk profiles.
- Catastrophe insurance. Weather sensors, drones, and satellite systems enable live monitoring of environmental conditions and early warnings for risks of floods, wildfires, hurricanes, etc. IoT technology also aids in damage assessment after disasters, optimizing claims processing and payouts.
Insurance Industry’s Challenges with IoT
Integration of IoT in insurance encounters the following hurdles and demands a well-thought strategy that balances benefits with risk mitigation.
Cybersecurity in IoT Systems
Despite being one of the top trends in insurance, IoT devices lack robust encryption and authentication while transmitting vast amounts of sensitive data. Its breach can lead to identity theft, fraud, or financial losses for both parties.
Hackers need only one vulnerable device in an IoT network to create an entry point for malicious attacks and expose, corrupt, or lock data. Additionally, cybercriminals can take control of devices, affecting claims settlement.
Data Accuracy
Sensors can experience hardware failures and calibration issues leading to incorrect readings, while unstable network connections may deliver incomplete or corrupted data.
Also, a lack of standardization across manufacturers can result in inconsistent or conflicting readings. Inaccurate data implies miscalculated premiums, claim disputes, and operational inefficiencies.
Malfunctioning Devices
Insurers rely on IoT data for underwriting, risk assessments, and evidence of claims. So, defective devices lead to mispriced policies, erroneous evaluations, claims disputes, customer dissatisfaction, and increased costs.
Using faulty IoT gadgets may cause legal action against insurers once they make unfair policy decisions. Sensors reporting false conditions and triggering payouts increase fraud risks.
The demand for IoT has been steadily growing since 2017 when an IoT startup from Switzerland turned to Mobulinity for rare, highly skilled tech talents specializing in embedded development, cloud computing, and hardware engineering.
The company was about to lose its key employees, who were being hunted by more established businesses, and it knew it would take months to find specialists of the same level in the local market.
Due to our personalized approach to every client, Mobilunity attracted new niche experts for this IoT provider and managed to retain previously hired IoT developers. Read more about the solutions we provided in the case study.
How to Enhance IoT-Powered Insurance Market with ML
To enhance the cybersecurity of IoT tools and customer trust, improve risk assessment and claims processing, and minimize the consequences of equipment malfunctions, insurance companies must introduce machine learning.
Here’s how it can help:
| Challenge of IoT | How ML Helps |
| Cyber attacks/Device tampering | Identifies and reports unusual patterns in IoT device activity |
| Data encryption | Optimizes and adapts encryption algorithms to detect risks Pinpoints and corrects abnormal readings |
| Checking data integrity and quality | Confirms logs by cross-referencing sensor data with policyholder activity Verifies data against other sources and contextual factors |
| Monitoring network traffic | Blocks unauthorized devices |
| Anticipating device failure | Ensures sensors are repaired and replaced before producing inaccurate data |
| Data standardization | Aligns data for consistent and accurate usage |
| Eliminating irrelevant or redundant data | Removes false alarms and other “noise” from the system |
| Identifying the malfunction cause | Facilitates quicker resolution |
Cloud Technology in Insurance
Here’s a list of benefits you get when using insurance cloud technology stacks:
Real-Time Access to Claims
Cloud solutions allow for the consolidation of customer, policy, and claims data into one repository. Employees, policyholders, and partners can access and share information on Azure, Google, or AWS Cloud platforms from anywhere round-the-clock, which is, for instance, exceptionally valuable for open insurance and embedded insurance.
Once your data volume grows, you can instantly extend storage facilities without expanding the physical infrastructure.
Building Global Insurance Platforms
With platforms like AWS, Azure, or CGP, insurers can host core applications and technology infrastructure required for their insurance software solutions.
With AWS developers, you can set up policy processing, underwriting, and claims management. They’ll help you leverage cloud computing in the insurance industry by establishing a robust data management system, ensuring seamless integration with existing systems, and protecting sensitive customer data.
Challenges of Cloud Adoption
Incorporation of cloud systems offers insurers positive returns from cloud technology investments but also comes with the following challenges.
Compliance with Local Data Protection Laws
Many countries require storage of an insurance company’s data, particularly PII, within their borders or imply additional obligations for cross-border transfers. However, cloud providers don’t always have data centers in needed jurisdictions which creates compliance risks.
Potentially High Costs of Switching to Cloud Services
Moving to the cloud can be costly if it requires complex data migration tools and specialized expertise. Also, adapting current insurance products or legacy apps to cloud environments may demand significant re-engineering and development efforts that imply additional expenses.
Challenges of Insurance Tech Trends Implementation
Solving the challenges is vital for adopting new technologies and incorporating digital transformation in insurance. Overcoming the implementation obstacles below will help companies leverage the full potential of insurtech.
Data Confidentiality
Insurers collect large volumes of sensitive PII with technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud services. Health data, financial records, etc., have become prime targets for cybercriminals.
Non-compliance with GDPR, CCPA, and other standards can lead to legal issues, while the risk of data sharing without explicit consent increases.
Solutions
- Invest in robust data encryption
- Develop access control mechanisms
- Run regular security audits
- Ensure data storage compliance with local data sovereignty laws
- Implement privacy-by-design principles.
Significant Expenses
Developing or purchasing new IoT, blockchain, or AI technology requires substantial investments. Costs grow more when companies need major upgrades of their legacy systems, further maintenance, and the purchase of security tools.
Implementing insurtech solutions requires hiring dedicated blockchain developers, data scientists, or AI experts, whose salaries are pretty high due to the strong market need for these specialists.
Solutions
- Prioritize areas and technologies that will yield the highest ROI
- Test a particular technology to assess its benefits, costs, and challenges
- Outsource specific tech-related functions.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Disparate data formats and structures, outdated security protocols, resistance to change, and skill gaps are the key issues in embracing insurtech solutions.
Companies need to migrate and clean data, build custom APIs, ensure seamless data flow while maintaining security standards, gain expertise, and adjust business processes. Such changes require considerable investments in software, personnel, and, sometimes, hardware.
Solutions
- Shift to cloud platforms to decrease infrastructure costs
- Implement insurtech technologies in phases
- Collaborate with insurtech firms
- Focus on process automation.
Lack of Skills
Many insurance professionals in traditional firms lack proficiency in AI, ML, data analytics, cybersecurity, and blockchain. The scarcity of training programs focusing on emerging technologies and the high costs of upskilling are the key constraints to adopting technology trends without new specialists.
However, the demand for technical professionals is high across all industries, so hiring skilled candidates for insurance projects is also challenging and cost-demanding.
Solutions
- Invest in training programs for insurance specialists
- Contract a remote dedicated development team
- Collaborate with academic institutions.
“In the DCFS survey, prioritizing candidates with digital literacy and AI knowledge for new job openings was the top-ranked change that respondents are making in terms of how they manage and hire talent to prepare for the long-term adoption of AI[…] Insurers may also choose to rely more heavily on outsourcing and shared services if they are unable to attract and develop their own internal talent in the short term.” (Deloitte)
Mobilunity has assembled a remote dedicated team of insurtech developers for esurance — a Swiss online insurance broker.
Here’s what Giles Magnin, Chief Product Officer at esurance, says about our cooperation (case study):
“We tried to hire devs in Switzerland for a very long time. We were lucky to find Mobilunity who recruited and hosts our nearshoring dev team in Kyiv. They allowed us to build up speed for a very good Price/Value ratio.”
Hiring providers can help you engage experienced engineers to meet your project requirements while fostering innovation and keeping up with the insurance tech trends.
Below are the key advantages of collaborating with a vendor.

Wrapping Up
Insurance technology trends drive efficiency, improve customer experiences, and enhance decision-making. Innovations like AI, RPA, IoT, blockchain, and cloud computing help companies adapt insurance value chains to market changes and foster digital evolution.
However, to make the most of the latest trends and stay within budget, insurance businesses need to consider hiring remote insurtech engineers with reliable providers.