EOR (Employer of Record)
Employer of Record Definition
Employer of Record or EOR stands for a third-party organization that acts on behalf of a client company as a legal employer of overseas workers with all core responsibilities, such as compliance, payroll, and withholdings. Utilizing a global employer of record (EOR) can streamline the process of hiring and managing international employees, ensuring compliance with local labor laws, handling payroll and benefits, and significantly reducing the administrative burden associated with expanding your workforce globally.
Employment of Record allows businesses to expand to new countries and markets without having a local entity. EOR is legally responsible for payroll, taxes, and employee benefits [1].
Employer of Record Takeaways:
- An employer of record company is a separate entity that takes over responsibilities of a legal employer of client’s workforce in another country;
- Employer of record services can be a part of global expansion strategy;
- EOR is responsible for payroll, compliance, and all obligations regarding employees;
- Day-to-day works of employees, as well as all decisions, are still held by the client company.
Why Companies Choose Employer of Record Services
As the employer of record meaning suggests, this practice exists so that a company could easily expand to new countries without breaking any legal restrictions or setting a legal entity there. It is a steadily growing market [2]. The main reasons for choosing an employer of record services are:
- A company wants to access a foreign market and workforce without committing to a legal entity or branch there. It is simply easier, faster, cost-effective, and holds fewer risks;
- Another country has unusual or extremely complex legislation when it comes to employment. The employer of record companies can manage those much more effectively as they have specific expertise.
- It is a part of a global expansion strategy with outsourcing BPO, administrative tasks, development projects, etc.
- A company wants to hire remote employees in another country and has to run local payroll.
- Registering a legal business entity takes much longer, and often cases are not reasonable.
Employment of record practice ensures all the benefits of outsourcing or remote work whilst saving money and time on registration or hiring local HR. It also ensures all legal compliances.
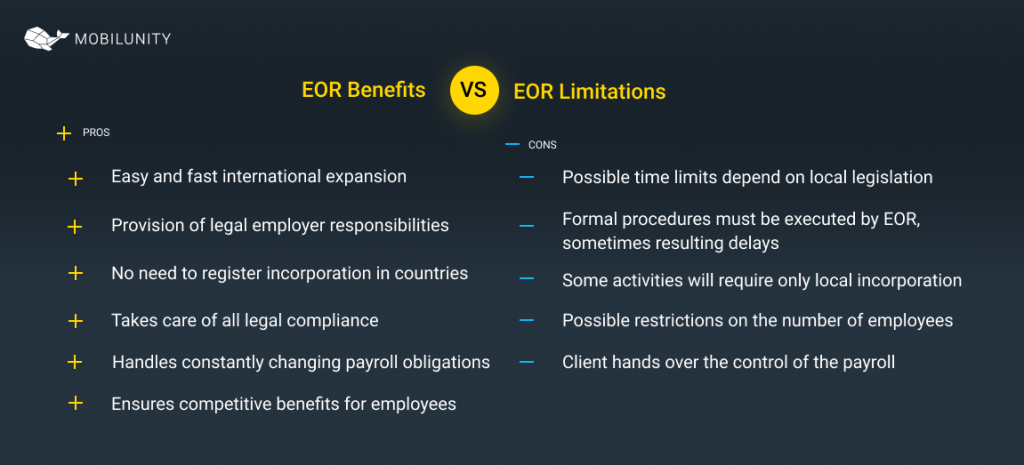
EOR Benefits and Limitations
After answering the question of what is an employer of record, it is necessary to highlight the advantages and limitations of such business practice. As with any other practice of this kind, like BPO[3] or RPO[4], it appeared as a solution for specific business needs. Whether employer of record services are applied internationally or locally (it is also an option), they offer such benefits:
- Easy and fast international expansion;
- Provision of legal employer responsibilities when accessing workforce in another country, which is usually the legal requirement;
- An employer of record company can act as a legal employer for workers in multiple countries without any need to set a local branch and register incorporation;
- The employer of record companies takes care of all legal compliance issues, including visa, immigration, work permit, and payroll.
- Such service providers handle constantly changing payroll obligations, health insurance requirements, and any tax issues.
- Employment of record ensures competitive benefits and insurance packages for employees to attract top talent. Otherwise, such an option can be inaccessible for small and medium-sized businesses.
Overall, EOR stands for cost-effective practice with no need for local incorporation. It ensures immigration compliance and local payroll compliance. But like any other practice, it has its limitation, namely:
- Possible time limits depend on local legislation. For example, in Germany, employees can work for EOR only for 18 months;
- Although employees work under the client’s supervision and management, formal procedures must be executed by EOR. It requires close cooperation with EOR HR, and sometimes it can result in delays;
- Some business activities will require only local incorporation;
- Some countries may have restrictions on the number of employees working through EOR.
- Client hands over the control of the payroll.
Responsibilities of an Employer of Record Company
So what is an employer of record responsible for exactly? Here is what an EOR does:
- Tax registration and management; it is registered by tax institutions and does all tasks involved;
- Payroll management according to legal requirements;
- Benefits management, such as contribution to pension funds or provision of health insurance for employees;
- Employment contract management, from hiring to terminations;
- Visa or work permit management;
- Advise the client of local employment limitations, like notice period or rules for termination;
- Becomes an interface not only between a client and employees and between the client and the local government.
Without an employer of record company, it wouldn’t be possible to employ a workforce in another country or state unless a company registers local legal entities. Although having a local branch might be reasonable for big corporations, it is risky and costly for smaller businesses.
Another alternative is working with foreign professionals like contractors, but it is never the best option due to many potential risks. EOR plays the role of legal entity in the foreign country and region and takes care of all employment-related tasks in compliance with local legislation.
How to Choose an Employer of Record Company
It is important to do due diligence and find the service provider that will fulfill all your requirements when it comes to business partners. Although the employer of record companies offer similar services, they have different prices, levels of expertise, and ways of work. To make an educated decision on an employer of record company answer these questions:
- Is this EOR provider global? Do they cover the countries you are interested in?
- Do they offer data and commercial interest protection? Such specifics must be clearly stated in a contract as they’ll have access to the sensitive data.
- How does this employer of record company deliver its services? What are the points of contact? Are they comfortable with your business practices?
- How long have they provided employer of record services? Is it an established and trusted business with a great track record?
- Have they worked in the same industry as you? Are similar companies among their clients? It will make sure they know the specifics of your core activity.
- Do they offer full-cycle EOR? Is it their core service or a side practice? It is always better to go for those who focus specifically on EOR.
- Are they compliant with both local and international legislation regarding employment record requirements [5]?
- How do they calculate fees? Is it a set rate per employee or a percent?
- How long is the contract duration? What are the terms of termination?
In the case of an employer of record services, a client company needs to ensure that all their interests are met and set in a bulletproof contract.
References
- https://dictionary.cambridge.org/us/dictionary/english/employer-of-record
- https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/toolkits/pages/complyingwithemploymentrecordrequirements.aspx
- https://mobilunity.com/blog/employer-of-record-services/
- https://mobilunity.com/offshoring-wiki/bpo-business-process-outsourcing/
- https://mobilunity.com/offshoring-wiki/rpo-recruiting-process-outsourcing/